Create a pipeline to run an end-to-end scenario to automate all or part of the AI lifecycle. For example, create a pipeline that creates and trains an asset, promotes it to a space, creates a deployment, then scores the model.
Watch this video to see how to create and run a sample pipeline.
This video provides a visual method to learn the concepts and tasks in this documentation.
Adding a pipeline to a project
Follow these steps to add a pipeline to a project:
-
Open a project.
-
Click New task > Automat model lifecycle.
-
Enter a name and optional description.
-
Click Create to open the canvas.
Pipeline access
When you use a pipeline to automate a flow, you must have access to all of the elements in the pipeline. Make sure that you create and run pipelines with the proper access to all assets, projects, and spaces used in the pipeline.
Best practice: Adding assets to a pipeline
When you create a pipeline, you add assets, such as data, notebooks, deployment jobs, or Data Refinery jobs to the pipeline to orchestrate a sequential process. The strongly recommended method for adding assets to a pipeline is to collect the assets in the project containing the pipeline and use the asset browser to select project assets for the pipeline.
Overview: Building a pipeline
Follow these high-level steps to build and run a pipeline.
- Drag any node objects onto the canvas. For example, drag a Run notebook job node onto the canvas.
- Use the action menu for each node to view and select options.
- Configure a node as required. You are prompted to supply required input options. For some nodes, you can view or configure output options as well. For examples of configuring nodes, see Configuring pipeline components.
- Drag from one node to another to connect and order the pipeline.
- Optional: Click the Global objects icon in the toolbar to configure runtime options for the pipeline.
- When the pipeline is complete, click the Run icon on the toolbar to run the pipeline. You can run a trial run to test the pipeline, or you can schedule a job when you are confident in the pipeline.
Configuring nodes
As you add nodes to a pipeline, you must configure them to provide all of the required details. For example, if you add a node to run an AutoAI experiment, you must configure the node to specify the experiment, load the training data, and specify the output file. For example:
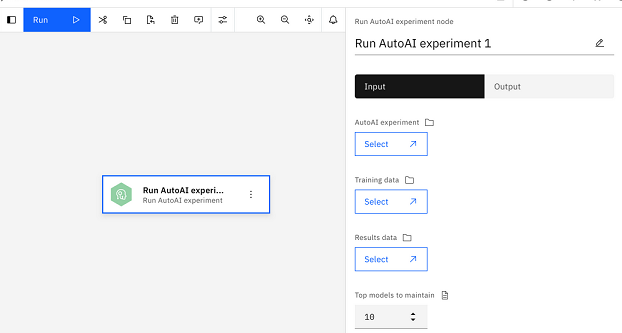
Connecting nodes
When you build a complete pipeline, the nodes must be connected in the order in which they should execute in the pipeline. To connect nodes, hover over a node and drag a connection to the target node. Disconnected nodes are executed in parallel.

Defining pipeline parameters
A pipeline parameter defines a global variable for the whole pipeline. Use pipeline parameters to specify data from one of these categories:
| Parameter type | Can specify |
|---|---|
| Basic | JSON types such as string, integer or a JSON object |
| CPDPath | Resources available within the platform, such as assets, asset containers, connections, notebooks, hardware specs, projects, spaces, or jobs |
| InstanceCRN | Storage, machine learning instances, and so on |
| Other | Various configuration types, such as status, timeout length, estimator, error policies and so on |
To specify a pipeline parameter:
- Click the global objects icon in the toolbar to open the Manage global objects window.
- Select Pipeline parameters tab to configure parameters.
- Click Add pipeline parameter.
- Specify a name and optional description.
- Select a type and provide any required information.
- Click Add when the definition is complete, and repeat previous steps until you finish defining parameters.
- Close the Manage global objects dialog.
The parameters are now available to the pipeline.
Saving a version of a pipeline
You can save a version of a pipeline and revert to it at a later time. For example, if you want to preserve a particular configuration before you make changes, save a version. You can revert the pipeline to a previous version. When you share a pipeline, the latest version is used.
To save a version:
- Click the Versions icon on the toolbar.
- In the Versions pane, click Save version to create a new version with a version number incremented by 1.
When you run the pipeline, you can choose from available versions.
Running a pipeline
The Run option gives you several options:
- Trial run runs the pipeline without creating a job. Use this to test a pipeline.
- Create a job presents you with an interface for configuring and scheduling a job to run the pipeline. You can save and reuse run details, such as pipeline parameters, for a version of your pipeline.
- View history compares all of your runs over time.
When you run a pipeline from a trial run or a job, click the node output to view the results of a successful run. If the run fails, error messages and logs are provided to help you correct issue.
- Errors in the pipeline are flagged with an error badge. Open the node or condition with an error to change or complete the configuration.
- Use the consolidated logs to review operations or identify issues with the pipeline.
Managing pipeline credentials
To run a job, the pipeline must have access to IBM Cloud credentials. Typically, a pipeline uses your personal IBM Cloud API key to execute long-running operations in the pipeline without disruption. If credentials are not available when you create the job, you are prompted to supply an API key or create a new one.
To generate an API key from your IBM Cloud user account, go to Manage access and users - API Keys and create or select an API key for your user account.
Alternatively, you can request that a key is generated for the pipeline. In either scenario, name and copy the key, protecting it as you would a password.
Next steps
Parent topic: IBM Watson Pipelines