You can integrate data into notebooks by accessing the data from a local file, from free data sets, or from a data source connection. You load that data into a data structure or container in the notebook, for example, a pandas.DataFrame, numpy.array, Spark RDD, or Spark DataFrame.
To work with data in a notebook, you can choose between the following options:
| Option | Recommended method | Requirements | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Add data from a file from your local system | Use generated code for the selected data source by clicking the Code snippets icon ( |
The file must exist as a project asset | Add a file from your local system |
| Add data from a free data set from the Samples | Use generated code for the selected data source by clicking the Code snippets icon ( |
The data set (file) must exist as a project asset | Use a free data set from the Samples |
| Load data from data source connections | Use generated code for the selected data source by clicking the Code snippets icon ( |
The connections must exist as project assets | Load data from a data source connection |
| Access project assets and metadata programmatically | Use ibm-watson-studio-lib |
The data sources must exist as project assets | Use the ibm-watson-studio-lib library to interact with data assets |
| Create and use feature store data | Use assetframe-lib library functions |
The data assets must exist as assets in the project | Use the assetframe-lib library for Python to create and use feature store data |
| Access data using an API function or operating system command | For example, use Wget |
N/A | Access data using an API function or operating system command |
Load data from local files
To access data from a local file, you can load the file from within a notebook, or first load the file into your project. From your notebook, you add automatically generated code to access the data by clicking the Code snippets icon (![]() ) and then clicking Read data. The generated code serves as a quick start to allow you to easily begin
working with data sets.
) and then clicking Read data. The generated code serves as a quick start to allow you to easily begin
working with data sets.
Code is generated for file types such as CSV, JSON, and XLSX. To learn which data structures are generated for which notebook language, see Data load support. For file types for which code generation is not supported, you can insert only the file credentials. With the credentials, you can write your own code to load the file data into a DataFrame or other data structure in a notebook cell.
To add a file from your local system to your notebook:
- Open your notebook in edit mode, click the Upload asset to project icon (
 ) from the
toolbar, and then browse a data file or drag it into your notebook sidebar.
) from the
toolbar, and then browse a data file or drag it into your notebook sidebar. - Click the Code snippets icon (
 ), click Read data and then select the data file from the
project. Use the pencil icon if you want to select a different data file.
), click Read data and then select the data file from the
project. Use the pencil icon if you want to select a different data file. - In the Load as drop-down list, select the load option that you prefer.
- Click in an empty code cell in your notebook and then click to insert the generated code. Alternatively, click to copy the generated code to the clipboard and then paste the code into your notebook.
To manually add file credentials and write code for the file access method and the DataFrame yourself:
- Add the file to your object storage by clicking the Upload asset to project icon (
 ),
and then browsing the data file or dragging it into your notebook sidebar.
),
and then browsing the data file or dragging it into your notebook sidebar. - Click the Code snippets icon (
 ) and then click Read data.
) and then click Read data. - Click in an empty code cell in your notebook, select the load option Credentials, and then load the credentials to the cell. You can also click to copy the credentials to the clipboard and then paste them into your notebook.
- Insert your credentials into the appropriate method for your notebook language to access the data in your notebook. For example, see this code in a blog for Python.
- Reference the data access method in the appropriate read method for your language to load the data into a DataFrame or other data structure.
Load data sets from the Samples
The data sets on the Samples contain open data. Watch this short video to see how to work with public data sets in the Samples.
This video provides a visual method to learn the concepts and tasks in this documentation.
To add a data set from the Samples in your notebook, you copy the data set into a project:
- From the IBM watsonx navigation menu, select Samples.
- Find the card for the data set that you want to add.
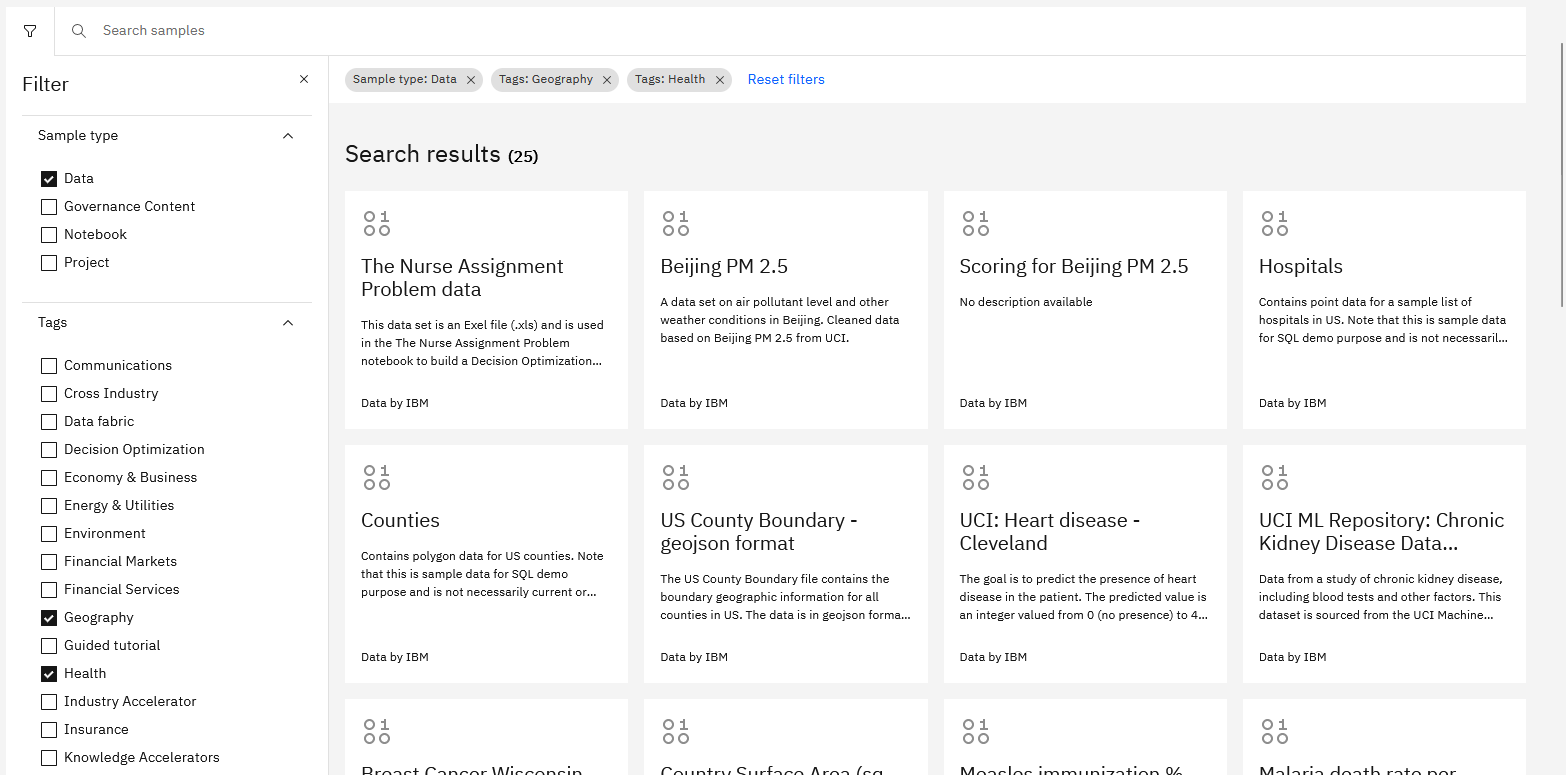
- Click Add to project, select the project, and click Add. Clicking View project takes you to the project Overview page. The data asset is added to the list of data assets on the project's Assets page.
- Open your notebook in edit mode, click the Code snippets icon (
 ) from the toolbar, click Read data and then select the data asset from the project.
) from the toolbar, click Read data and then select the data asset from the project. - In the Load as drop-down list, select the load option that you prefer.
- Click in an empty code cell in your notebook and then click to insert the generated code. Alternatively, click to copy the generated code to the clipboard and then paste the code into your notebook. The generated code serves as a quick start to begin working with a data set or connection. For production systems, carefully review the inserted code to determine whether you should write your own code that better meets your needs.
Load data from data source connections
Before you can load data from an IBM data service or from an external data source, you must create or add a connection to your project. See Adding connections to projects.
You add automatically generated code to load data from database connections by clicking the Code snippets icon (![]() )
from the notebook toolbar and then clicking Read data. To learn which database connections are supported, see Data load support. For database connections that are not supported,
you can insert only the database connection credentials. With the credentials, you can write your own code to load the data into a DataFrame or other data structure in a notebook cell.
)
from the notebook toolbar and then clicking Read data. To learn which database connections are supported, see Data load support. For database connections that are not supported,
you can insert only the database connection credentials. With the credentials, you can write your own code to load the data into a DataFrame or other data structure in a notebook cell.
To load data from an existing data source connection into a data structure in your notebook:
- Open your notebook in edit mode, click the Code snippets icon (
 ) from the toolbar, click Read data and then select a data source connection from the project. Use the pencil icon if you want to select a different connection.
) from the toolbar, click Read data and then select a data source connection from the project. Use the pencil icon if you want to select a different connection. - Select the schema and choose a table. Use the pencil icon if you want to change your selection.
- Select the load option. If you select credentials and not a data load option after you choose the schema and table, only metadata will be generated.
- Click in an empty code cell in your notebook and then insert code to the cell. Alternatively, click to copy the generated code to the clipboard and then paste the code into your notebook. The generated code serves as a quick start to begin working with a data set or connection. For production systems, carefully review the inserted code to determine whether you should write your own code that better meets your needs.
- If necessary, enter your personal credentials for locked data connections that are marked with a key icon (
 ). This is a one-time
step that permanently unlocks the connection for you. After you have unlocked the connection, the key icon is no longer displayed. See Adding connections to projects.
). This is a one-time
step that permanently unlocks the connection for you. After you have unlocked the connection, the key icon is no longer displayed. See Adding connections to projects. - If no code can be generated for the connection, load the credentials and open the database connection that references your credentials. Write code to load the data.
Use an API function or operating system command to access the data
You can use API functions or operating system commands in your notebook to access data, for example, the Wget command to access data by using the HTTP, HTTPS or FTP protocols. When you use these types of API functions and commands,
you need to include code that sets the project access token. See Manually add the project access token.
Learn more
-
Use the ibm-watson-studio-lib library to interact with project assets programmatically. The
ibm-watson-studio-liblibrary is the successor ofproject-lib. To move fromproject-libto usingibm-watson-studio-lib, see:
Parent topic: Notebooks and scripts