You can integrate data into notebooks by accessing the data from a local file, from free data sets, or from a data source connection. You load that data into a data structure or container in the notebook, for example, a pandas.DataFrame, numpy.array, Spark RDD, or Spark DataFrame.
To work with data in a notebook, you can choose between the following options:
| Option | Recommended method | Requirements | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Add data from a file on your local system | Add a Code snippet that loads your data | The file must exist as an asset in your project | Add a file from your local system and then Use a code snippet to load the data |
| Add data from a free data set from the Resource hub | Add a Code snippet that loads your data | The data set (file) must exist as an asset in your project | Add a free data set from the Resource hub and then Use a code snippet to load the data |
| Load data from data source connections | Add a Code snippet that loads your data | The connection must exist as an asset in your project | Add a connection to your project and then Add a code snippet that loads the data from your data source connection |
| Access project assets and metadata programmatically | Use ibm-watson-studio-lib |
The data asset must exist in your project | Use the ibm-watson-studio-lib library to interact with data assets |
| Create and use feature store data | Use assetframe-lib library functions |
The data asset must exist in your project | Use the assetframe-lib library for Python to create and use feature store data |
| Access data using an API function or an operating system command | For example, use wget |
N/A | Access data using an API function or an operating system command |
Adding a file from your local system
To add a file from your local system to your project by using the Jupyterlab notebook editor:
- Open your notebook in edit mode.
- From the toolbar, click the Upload asset to project icon
 and add your file.
and add your file.
Load data sets from the Resource hub
The data sets on the Resource hub contain open data. Watch this short video to see how to work with public data sets in the Resource hub.
This video provides a visual method to learn the concepts and tasks in this documentation.
-
Video transcript Time Transcript 00:00 This video shows you how to access public data sets in the Cloud Pak for Data as a Service Gallery. 00:06 Start in the Resource Hub and use the filters to see just the data sets. 00:13 Here, you'll find some rich data sets for you to use in your analysis. 00:17 For example, you can search for "economy" or "population" or "weather" or "jobs". 00:28 This looks like an interesting data set. 00:30 Open it and preview the data. 00:34 From here, you can share the data set on social media, get a direct link to the data set, or download the data set. 00:45 You can also copy the data set into a specific project. 00:52 Now, navigate to that project. 00:55 And on the "Assets" tab, you'll see the data set was added to the data assets section. 01:01 Next, add a new notebook. 01:05 The title for this notebook will be "Unemployment rates". 01:09 Select a runtime environment and a language. 01:14 When you're ready, create the notebook. 01:20 When the notebook loads, access the data sources and locate the unemployment file. 01:27 Click "Insert to code" and choose how you want to insert the data. 01:33 The choices in this drop-down box are dependent upon the language used in this notebook. 01:38 Notice that the inserted code includes the credentials you'll need to read the data file from the Object Storage instance. 01:45 When you run the code, the first five rows display. 01:50 Now, you're ready to start analyzing any of the rich data sets in the Resource Hub. 01:56 Find more videos in the Cloud Pak for Data as a Service documentation.
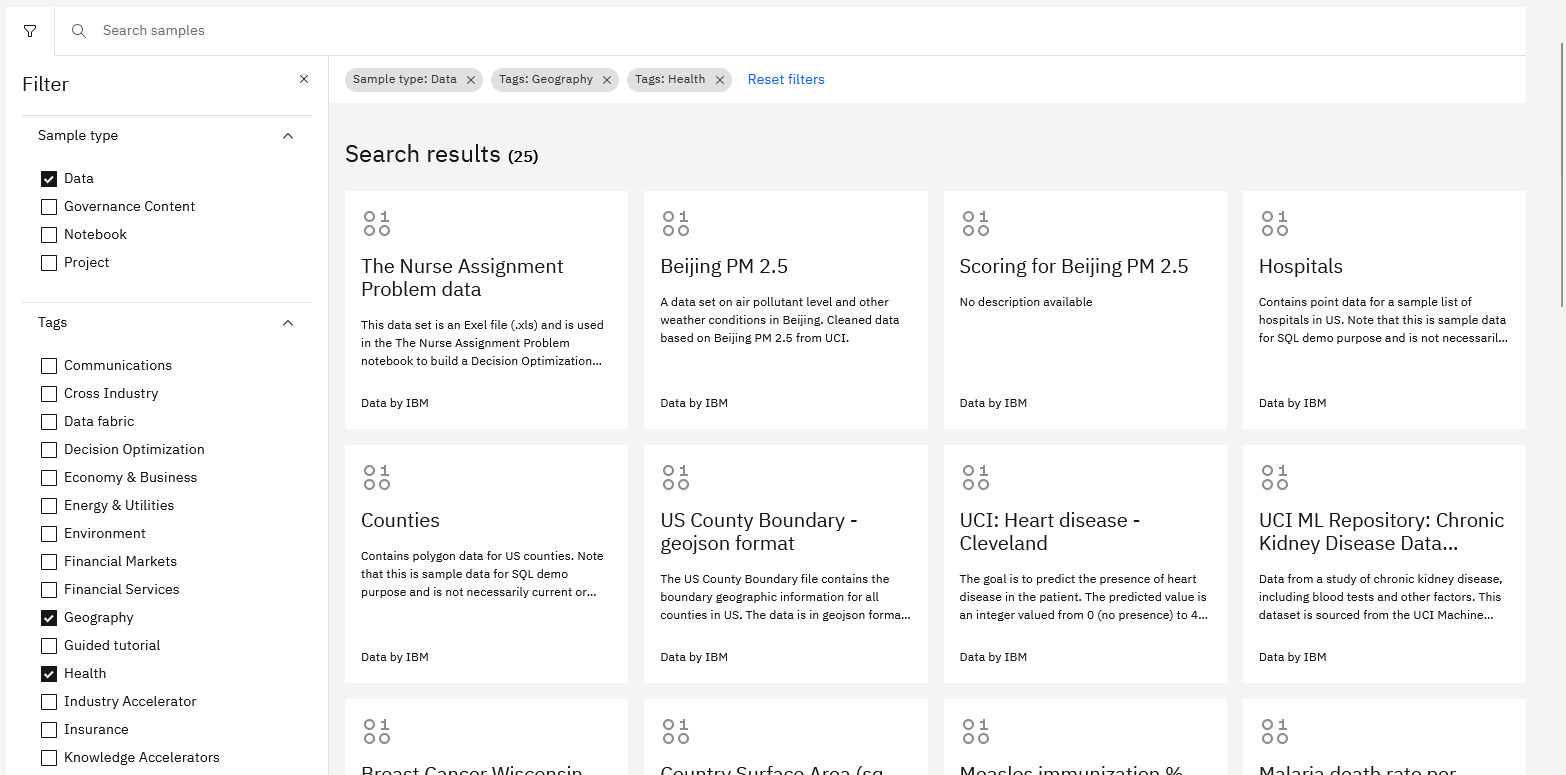
To add a data set from the Resource hub to your project:
-
From the navigation menu, select Resource hub.
-
Find the card for the data set that you want to add.
-
Click Add to project, select the project, and click Add. Clicking View project takes you to the project Overview page. The data asset is added to the list of data assets on the project's Assets page.
Loading data from files
Prerequisites The file must exist as an asset in your project. For details, see Adding a file from your local system or Loading a data set from the Resource hub.
To load data from a project file to your notebook:
- Open your notebook in edit mode.
- Click the Code snippets icon
 , click Read data, and then select the data file from your project.
If you want to change your selection, use Edit icon.
, click Read data, and then select the data file from your project.
If you want to change your selection, use Edit icon. - From the Load as drop-down list, select the load option that you prefer. If you select Credentials, only file access credentials will be generated. For details, see Adding credentials.
- Click in an empty code cell in your notebook and then click Insert code to cell to insert the generated code. Alternatively, click to copy the generated code to the clipboard and then paste the code into your notebook.
The generated code serves as a quick start to begin working with a data set. For production systems, carefully review the inserted code to determine whether to write your own code that better meets your needs.
To learn which data structures are generated for which notebook language and data format, see Data load support.
Loading data from data source connections
Prerequisites Before you can load data from an IBM data service or from an external data source, you must create or add a connection to your project. See Adding connections to projects.
To load data from an existing data source connection into a data structure in your notebook:
- Open your notebook in edit mode.
- Click the Code snippets icon
 , click Read data, and then select the data source connection from
your project.
, click Read data, and then select the data source connection from
your project. - Select the schema and choose a table. If you want to change your selection, use the Edit icon.
- Select the load option. If you select Credentials, only metadata will be generated. For details, see Adding credentials.
- Click in an empty code cell in your notebook and then insert code to the cell. Alternatively, click to copy the generated code to the clipboard and then paste the code into your notebook.
- If necessary, enter your personal credentials for locked data connections that are marked with the Key icon
 . This
is a one-time step that permanently unlocks the connection for you. After you unlock the connection, the key icon is no longer displayed. For more information, see Adding connections to projects.
. This
is a one-time step that permanently unlocks the connection for you. After you unlock the connection, the key icon is no longer displayed. For more information, see Adding connections to projects.
The generated code serves as a quick start to begin working with a connection. For production systems, carefully review the inserted code to determine whether to write your own code that better meets your needs.
You can find information about individual connection properties at https://dataplatform.cloud.ibm.com/connections/docs.
To learn which data structures are generated for which notebook language and data format, see Data load support.
Adding credentials
You can generate your own code to access the file located in your IBM Cloud Object Storage or a file accessible through a connection. This is useful when, for example, your file format is not supported by the snippet generation tool. With the credentials, you can write your own code to load the data into a data structure in a notebook cell.
To add the credentials:
- Click the Code snippets icon
 and then click Read data.
and then click Read data. - Click in an empty code cell in your notebook, select Credentials as the load option, and then load the credentials to the cell. You can also click to copy the credentials to the clipboard and then paste them into your notebook.
- Insert your credentials into the code in your notebook to access the data. For example, see this code in a blog for Python.
Use an API function or an operating system command to access the data
You can use API functions or operating system commands in your notebook to access data, for example, the wget command to access data by using the HTTP, HTTPS or FTP protocols. When you use these types of API functions and commands,
you must include code that sets the project access token. See Manually add the project access token.
For reference information about the API, see Data and AI Common Core API.
Parent topic: Notebooks and scripts