Once the Introduction to Modeling flow loads, you can see that part of the SPSS Modeler flow is already set up.
To build a flow and create a model, you need at least three nodes: a Data Asset node, a Type node, and a modeling node. Optionally, you can also add Table or Analysis nodes.
- Data Asset node
- This node reads data from an external source, in this case the tree_credit.csv data file. If you specify measurements in the source node, you don’t need to include a separate Type node in the flow.
- Type node
- This node specifies field properties, such as measurement level (the type of
data that the field contains), and the role of each field as a target or input in modeling. The
measurement level is a category that indicates the type of data in the field. The source data file
uses three different measurement levels:
- A Continuous field (such as the
Agefield) contains continuous numeric values. - A Nominal field (such as the
Educationfield) has two or more distinct values—in this caseCollegeorHigh school. - An Ordinal field (such as the
Income levelfield) describes data with multiple distinct values that have an inherent order—in this caseLow,Medium, andHigh.
Figure 2. Setting the target and input fields with the Type node 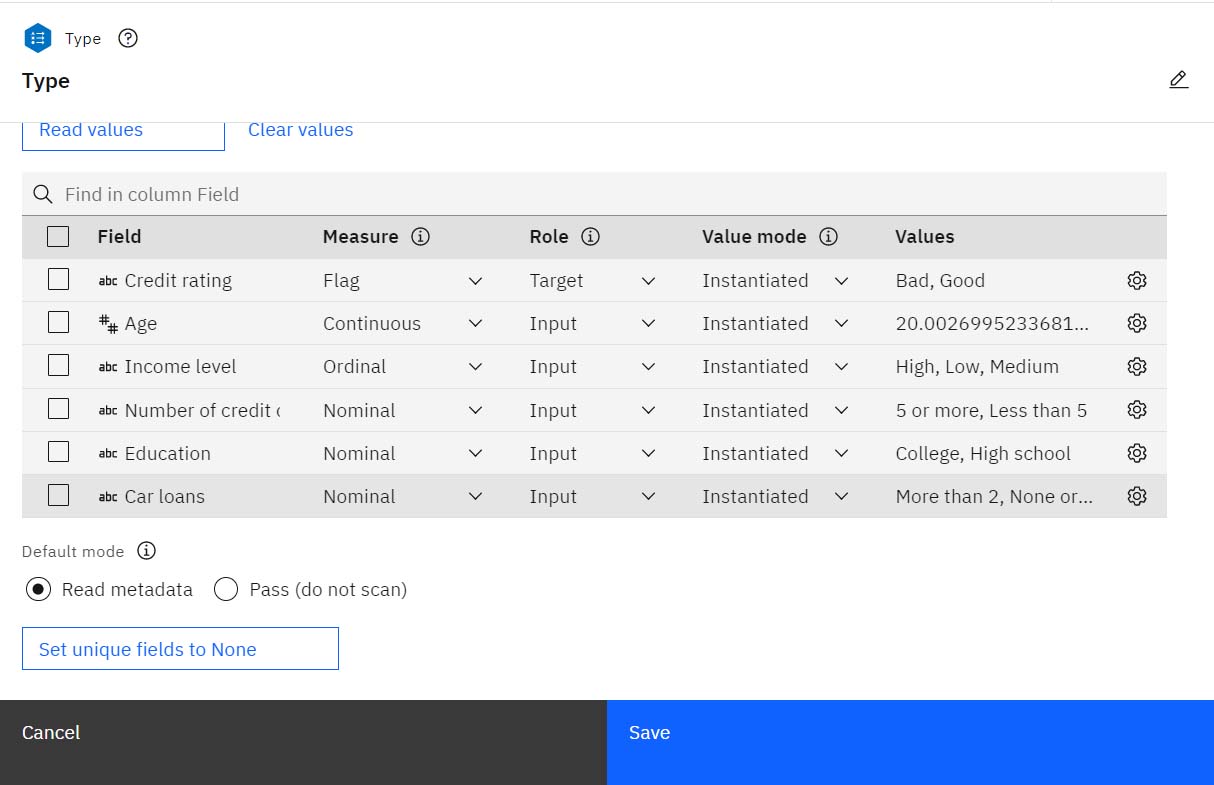
For each field, the Type node also specifies a role to indicate the part that each field plays in modeling. The role is set to
Targetfor the fieldCredit rating, which is the field that indicates whether a customer defaulted on the loan. Thetargetis the field for which you want to predict the value.Role is set to
Inputfor the other fields. Input fields are sometimes known aspredictors, or fields whose values are used by the modeling algorithm to predict the value of the target field. - A Continuous field (such as the
- Modeling node
-
A modeling node generates a model nugget when the flow runs. This example uses a CHAID node. CHAID, or Chi-squared Automatic Interaction Detection, is a classification method that builds decision trees by using a particular type of statistics that are known as chi-square statistics. The node uses chi-square statistics to work out the best places to make the splits in the decision tree.
The CHAID modeling node generates the model. In the node's properties, under FIELDS, the option to Use custom field roles is available. You could select this option and change the field roles. However, in this example, use the default targets and inputs as specified in the Type node.
- Table or Analysis nodes
- These nodes are optional. You can connect a Table or Analysis node to the model nugget to view the scoring results after the model nugget is added to the flow.
The three main nodes are already connected. So, all you need to do is configure the CHAID node.
- Double-click the CHAID node (named
Creditrating). The node properties are displayed.
Figure 3. CHAID modeling node properties 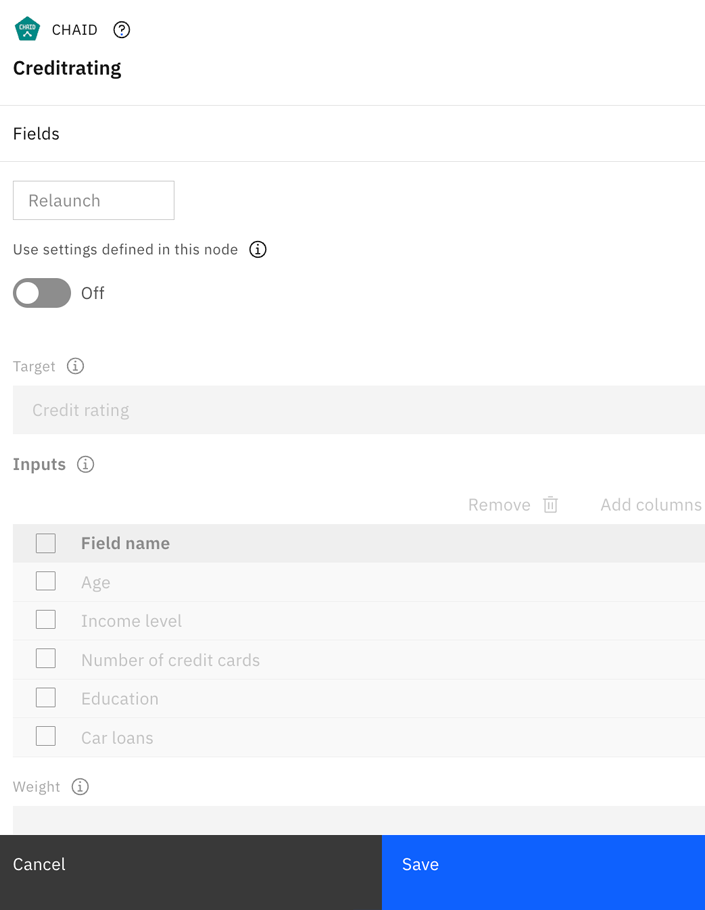
The CHAID node has several options where you could specify the kind of model you want to build.
For this example, the goal is to create a brand-new model. Under OBJECTIVES use the default Build new model option.
To create a single, standard decision tree model without any enhancements, use the default objective option Create a standard model.
Figure 4. CHAID modeling node objectives 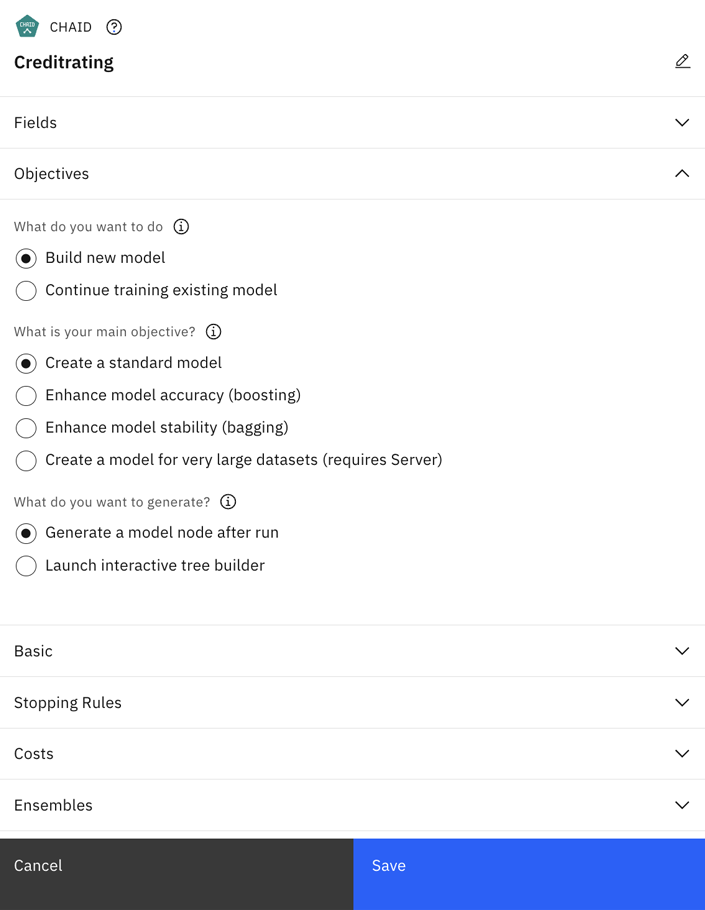
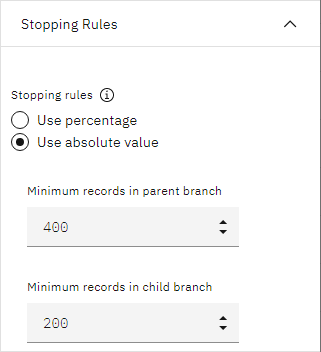
To keep the tree fairly simple for this example, limit the tree growth by raising the minimum number of cases for parent and child nodes.
- Under STOPPING RULES, select Use absolute value.
- Set Minimum records in parent branch to 400.
- Set Minimum records in child branch to 200.
You can use all the other default options for this example, so click
Save and then click the Run on the toolbar to create
the model. Alternatively, hover over the CHAID node
and click the Run icon ![]() .
.