This Decision
Optimization
Modeling Assistant example shows you how to create advanced
custom constraints that use Python.
Before you begin
Open any Decision
Optimization model in the Decision
Optimization
Modeling Assistant. This example uses the Shift
Assignment sample, that is available in the DO-samples, and uses the
AssignmentWithOnCallDuties scenario. The AssignmentWithCustomRule
scenario in this same sample shows you the completed model with this custom constraint already
added.
About this task
The Modeling Assistant provides you with
many constraint suggestions for your problem domain which can be customized. You might, however,
want to express constraints beyond those that are predefined for the given domains. You can achieve
this by using more advanced custom constraints that use Python DOcplex. This
example illustrates how you can create these.
Video disclaimer: Some minor steps and graphical steps in this video might
differ from your platform. The user interface is also frequently improved.
Read more in this Decision Optimization blog on custom constraints with Python
found on the IBM Data Science community page.
Note: To create and run Optimization models, you must have
both a
Machine Learning service added to your project and a
deployment space that is associated with your
experiment:
- Add a Machine Learning service to
your project. You can either add this service at the project level (see Creating a
Watson Machine Learning Service instance), or you can add it
when you first create a new Decision
Optimization
experiment: click Add a Machine Learning service, select, or create a
New service, click Associate, then close the
window.
- Associate a deployment space with your Decision
Optimization
experiment (see Deployment
spaces). A deployment space can be created or selected when you first create a new Decision
Optimization
experiment: click Create a deployment
space, enter a name for your deployment space, and click Create.
For existing models, you can also create, or select a space in the Overview information pane.
Procedure
To create a new advanced custom constraint:
-
In the Build model
view of your open Modeling Assistant model, look at the Suggestions
pane. If you have Display by category selected, expand the
Others section to locate New custom constraint, and click it to
add it to your model. Alternatively, without categories displayed, you can enter, for example,
custom in the search field to find the same suggestion and click it to add it
to your model.
A new custom constraint is added to your model.

- Click Enter your constraint. Use [brackets] for data, concepts, variables, or
parameters and enter the constraint you want to specify. For example, type
No [employees] has [onCallDuties] for more than [2] consecutive days and
press enter.
The specification is displayed with default parameters
(
parameter1, parameter2, parameter3) for you to customize. These parameters will be
passed to the Python function that implements this custom rule.

- Edit the default parameters in the specification to give them more meaningful names. For
example, change the parameters to
employees, on_call_duties, and
limit and click enter.
- Click function name and enter a name for the function. For example, type
limitConsecutiveAssignments and click enter.
Your function
name is added and an
Edit Python button appears.

- Click the Edit Python button.
A new window opens
showing you Python code that you can edit to implement your custom rule. You can see your customized
parameters in the code as follows:
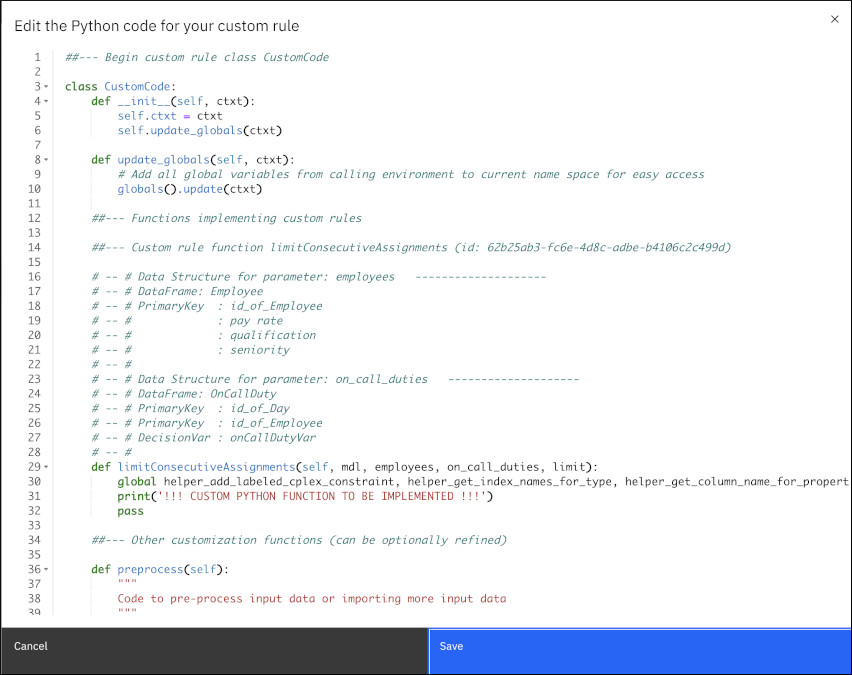
Notice that the code is documented
with corresponding data frames and table column names as you have defined in the custom rule. The
limit is not documented as this is a numerical value.
- Optional: You can edit the Python code directly in this window, but you might find it
useful to edit and debug your code in a notebook before using it here. In this case, close this
window for now and in the Scenario pane, expand the
three vertical dots and select Generate a notebook for this scenario that
contains the custom rule. Enter a name for this notebook.
The notebook is created
in your project assets ready for you to edit and debug. Once you have edited, run and debugged it
you can copy the code for your custom function back into this Edit Python
window in the Modeling Assistant.
- Edit the Python code in the Modeling Assistant
custom rule Edit Python window.
For example, you can define
the rule for consecutive days in Python as follows:
def limitConsecutiveAssignments(self, mdl, employees, on_call_duties, limit):
global helper_add_labeled_cplex_constraint, helper_get_index_names_for_type, helper_get_column_name_for_property
print('Adding constraints for the custom rule')
for employee, duties in employees.associated(on_call_duties):
duties_day_idx = duties.join(Day) # Retrieve Day index from Day label
for d in Day['index']:
end = d + limit + 1 # One must enforce that there are no occurence of (limit + 1) working consecutive days
duties_in_win = duties_day_idx[((duties_day_idx['index'] >= d) & (duties_day_idx['index'] <= end)) | (duties_day_idx['index'] <= end - 7)]
mdl.add_constraint(mdl.sum(duties_in_win.onCallDutyVar) <= limit)
- Click the Run button to run your model with your custom
constraint.
When the run is completed you can see the results in the
Explore solution
view.



